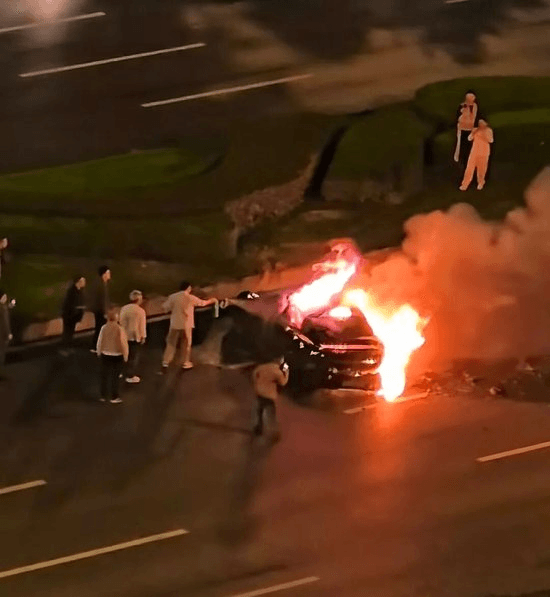Featured Story
Alibaba Launches Robotics and Embodied AI
Alibaba Group has set up a dedicated Robotics and Embodied AI team, signaling its entry into the fast-growing race among global tech giants to bring artificial intelligence into the physical world.

News
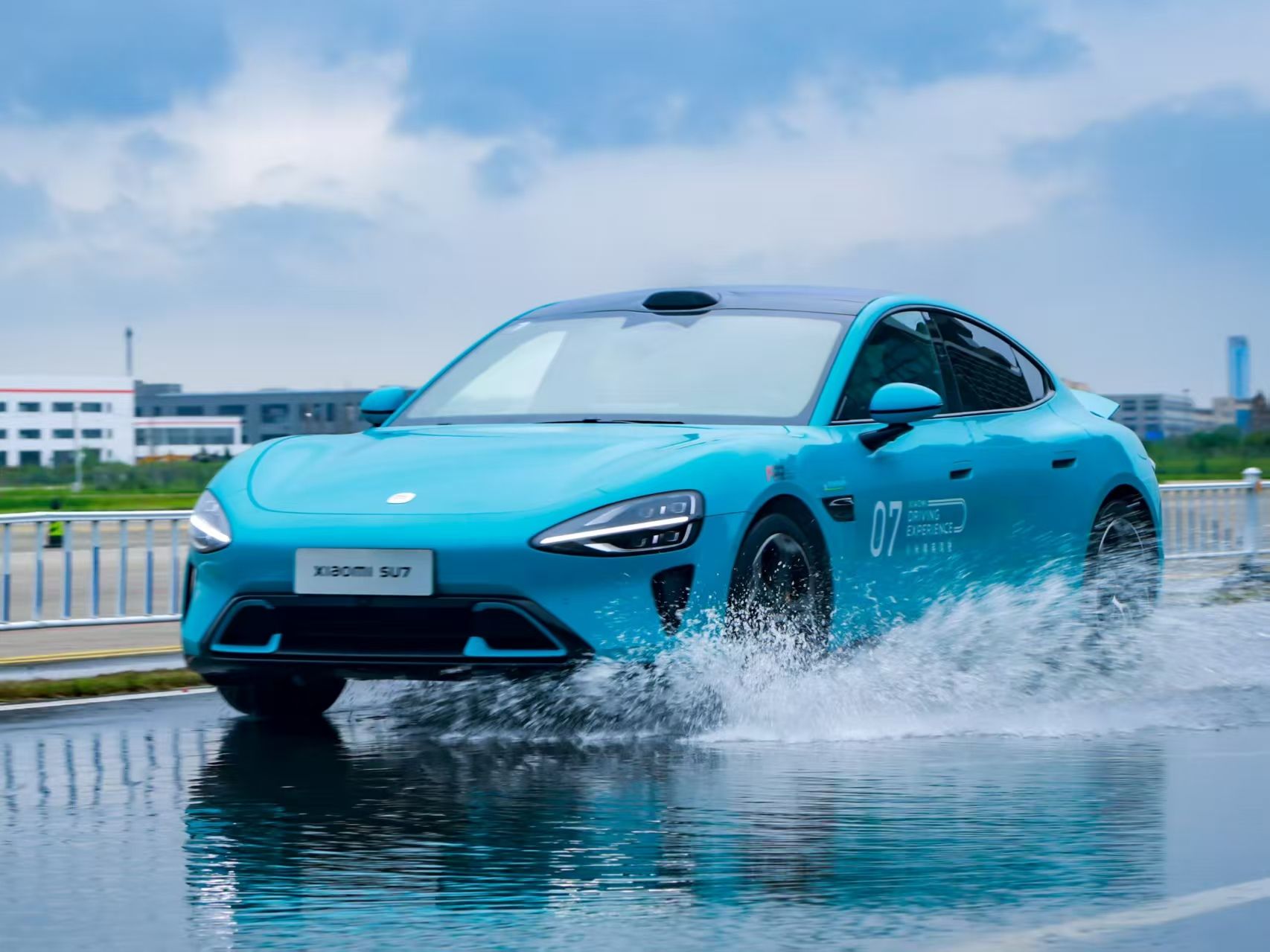
Xiaomi Responds to Incident of Car Reportedly Driving Off on Its Own

AI
Afari Technology Unveils AI Plan and New Brand

Industry
ByteDance’s Doubao Translation Model Supports 28 Languages, Performance Comparable to GPT-4o
ByteDance debuts Doubao translation model: two-way across 28 languages, performance comparable to GPT-4o, with fluent output and 4K context.

WAIC2025
Zhipu AI Launches GLM‑4.5, an Open-Source 355B AI Model Aimed at AI Agents
Chinese startup Zhipu AI (now rebranded as Z.ai) has open-sourced its new flagship model GLM‑4.5, a 355-billion-parameter foundation AI model. The July 28 ann...
WAIC2025
China Proposes “World AI Cooperation Organization” at WAIC 2025
Shanghai, July 28, 2025 – At the 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC) in Shanghai, the Chinese government announced an initiative to establish a...
Latest News
Xiaomi SU7 Bursts Into Flames After Crash in Chengdu, Driver Killed Despite Rescue Attempts
At around 3:16 a.m. on October 13, 2025, a severe traffic accident involving a Xiaomi SU7 occurred on the Tianfu Avenue section near Shigao, Renshou County, Chengdu, Sichuan Province.
Tencent Ushers in the AI Animation Era with 10 Million Views in Four Days
With a tenfold reduction in costs and a threefold increase in efficiency, China’s tech giant Tencent has released two AI-generated animated dramas, which have surpassed 10 million total views across platforms in just four days.
China’s Mega Holiday: Record Travel but Tighter Wallets
China’s 8-day National Day and Mid-Autumn holiday (Sep 29-Oct 6, 2025) saw record-breaking travel activity, with 2.43 billion cross-region trips (avg. 304M dail...
Didi Autonomous Driving Secures 2 Billion RMB in Series D Funding
Didi Autonomous Driving secured 2 billion RMB in Series D funding on October 11, 2025, to advance L4 autonomous technology and AI, with plans for demonstration applications in Beijing and Guangzhou by late 2025.
Reports: Microsoft Shanghai Layoffs Offer N+4 Severance, Relocation to Australia Option
Microsoft’s Shanghai teams, primarily Azure cloud, face layoffs with an N+4 severance package and an option to relocate to Australia, part of a global restructuring cutting over 15,000 jobs since May 2025.
BYD Rolls Out 14 Millionth NEV at Brazilian Plant, Marking New Global Phase
CAMAÇARI, Brazil – BYD marked a significant global expansion milestone with its 14 millionth new energy vehicle (NEV) produced at its Brazilian passenger car fa...
Vivo Unveils BlueLM 3B, an On-Device Multimodal Model that Ranks No.1 among Sub-10B Models
Vivo launches BlueLM 3B, an on-device multimodal model that claims No.1 among sub-10B models, with 128K context and unified “One Model” capabilities.
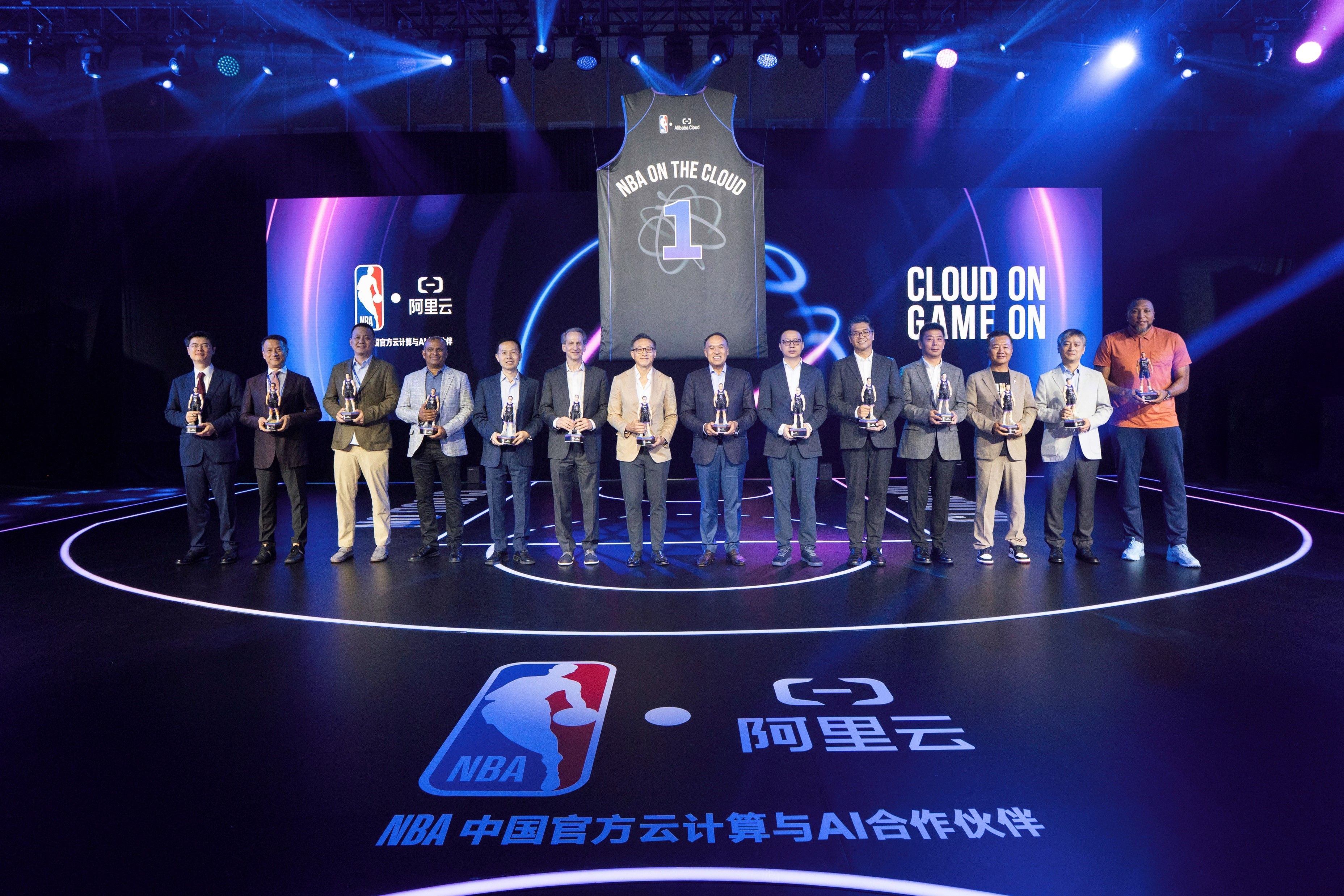
Alibaba Cloud Announces Multiyear Collaboration with NBA China to Reimagine Fan Engagement with AI
Alibaba Cloud and NBA China sign a multiyear deal to power AI-driven fan experiences, including a Qwen-based model and Real-Time 360 Replay.
Featured News
Stay Updated
Get the latest China tech news delivered to your inbox